|
|
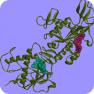 The SARS-CoV-2 nonstructural protein 14 (NSP14) is bifunctional protein with a proofreading and methylase activity and is essential in coronavirus biology. The NSP14 contains 3′-to-5′ exoribonuclease (ExoN) and guanine-N7-methyltransferase (N7-MTase) domains. Identification of small compounds that specifically target NSP14 is promising for anti-coronavirus drug discovery. The SARS-CoV-2 nonstructural protein 14 (NSP14) is bifunctional protein with a proofreading and methylase activity and is essential in coronavirus biology. The NSP14 contains 3′-to-5′ exoribonuclease (ExoN) and guanine-N7-methyltransferase (N7-MTase) domains. Identification of small compounds that specifically target NSP14 is promising for anti-coronavirus drug discovery.
|
|
Read more...
|
|
|
 The SARS-CoV-2 RNA uridylate‐specific endoribonuclease (non-structural protein 15, NSP15, NSP15/NendoU) is essential in coronavirus biology. It has an RNA endonuclease activity producing 2′‐3′ cyclic phosphodiester and 5′‐hydroxyl termini. Identification of small compounds that specifically target NSP15 is promising for antiviral drug discovery. The SARS-CoV-2 RNA uridylate‐specific endoribonuclease (non-structural protein 15, NSP15, NSP15/NendoU) is essential in coronavirus biology. It has an RNA endonuclease activity producing 2′‐3′ cyclic phosphodiester and 5′‐hydroxyl termini. Identification of small compounds that specifically target NSP15 is promising for antiviral drug discovery.
|
|
Read more...
|
|
 The SARS-CoV-2 helicase (non-structural protein 13, NSP13) is essential for coronaviral replication. It separates double-stranded RNA (dsRNA). Identification of small molecules that specifically target replication apparatus has indicated highest potential towards antiviral drug discovery. The SARS-CoV-2 helicase (non-structural protein 13, NSP13) is essential for coronaviral replication. It separates double-stranded RNA (dsRNA). Identification of small molecules that specifically target replication apparatus has indicated highest potential towards antiviral drug discovery.
|
|
Read more...
|
|
 The SARS-CoV-2 papain-like protease (PLpro) is a part of NSP3 multi-domain protein. It is essential for coronaviral replication. PLpro has also the additional function - stripping ubiquitin and ISG15 from host-cell proteins to aid coronaviruses in their evasion of the host innate immune responses. Thereby this enzyme is an attractive antiviral drug target. The SARS-CoV-2 papain-like protease (PLpro) is a part of NSP3 multi-domain protein. It is essential for coronaviral replication. PLpro has also the additional function - stripping ubiquitin and ISG15 from host-cell proteins to aid coronaviruses in their evasion of the host innate immune responses. Thereby this enzyme is an attractive antiviral drug target.
|
|
Read more...
|
|
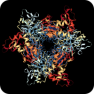
 2′-O-methyltransferase (2′-O-MTase, non-structural protein 16, nsp16) provides the viral mRNA with the ability to camouflage and obscure itself from the host cell, thus preventing recognition and activation of the host immune response which is essential for successful viral infection. Therefore, this protein can act as potential drug target for the SARS-CoV-2. 2′-O-methyltransferase (2′-O-MTase, non-structural protein 16, nsp16) provides the viral mRNA with the ability to camouflage and obscure itself from the host cell, thus preventing recognition and activation of the host immune response which is essential for successful viral infection. Therefore, this protein can act as potential drug target for the SARS-CoV-2.
|
|
Read more...
|
|
 An outbreak of COVID-19 (coronavirus disease 2019) occurred in Wuhan and it has rapidly spread to almost all parts of the world. For severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRP, RDR or RNA replicase) is an important enzyme that catalyzes the replication of RNA from RNA template and is an attractive therapeutic target. An outbreak of COVID-19 (coronavirus disease 2019) occurred in Wuhan and it has rapidly spread to almost all parts of the world. For severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRP, RDR or RNA replicase) is an important enzyme that catalyzes the replication of RNA from RNA template and is an attractive therapeutic target.
|
|
Read more...
|
|
 The COVID-19 pandemic caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is a global health emergency. An attractive drug target for this coronavirus is the main protease (3C-like proteinase, 3CLpro, Mpro) because of its essential role in processing the polyproteins that are translated from the viral RNA. The COVID-19 pandemic caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is a global health emergency. An attractive drug target for this coronavirus is the main protease (3C-like proteinase, 3CLpro, Mpro) because of its essential role in processing the polyproteins that are translated from the viral RNA.
|
|
Read more...
|
|
 Machine learning (ML) is advancing various industries, including drug discovery. We applied ML for predicting compounds with anti-SARS activity, which can be used for drug discovery projects related with COVID-19. Machine learning (ML) is advancing various industries, including drug discovery. We applied ML for predicting compounds with anti-SARS activity, which can be used for drug discovery projects related with COVID-19.
|
|
Read more...
|
|
|
|
|
|
 HOME
HOME ABOUT
ABOUT
 SERVICES
SERVICES
 PRODUCTS
PRODUCTS
 Targeted Libraries
Targeted Libraries
 Biochemicals
Biochemicals
 RESEARCH
RESEARCH
 DOWNLOADS
DOWNLOADS ORDERING
ORDERING
 CONTACTS
CONTACTS









