|

The OTAVA GPCR Antagonist Library is a computationally designed collection created to explore GPCR-privileged chemical space with a focus on antagonist and inverse-agonist pharmacology.
The library integrates ligand-based machine learning, Bayesian modeling, and AI-driven scaffold optimization to enable efficient discovery of structurally diverse GPCR antagonists.
|
|
Read more...
|
|
 It is proved that a diverse compound library is the most successful and straightforward starting point to find new leads. Moreover, it is the best way to enhance your research compound collections by adding new substances with different chemotypes. It is proved that a diverse compound library is the most successful and straightforward starting point to find new leads. Moreover, it is the best way to enhance your research compound collections by adding new substances with different chemotypes.
|
|
Read more...
|

We’re excited to introduce a powerful enhancement to your compound discovery workflow. A curated subset of OTAVA’s CHEMRIYA™ Virtual Chemical Space — comprising 1.4 billion synthetically feasible small molecules (just 2.5% of our total 55+ billion compound collection) — is now fully searchable through the AI-powered CHEESE Search platform.
This seamless integration enables researchers to explore the richness and diversity of CHEMRIYA™ using three orthogonal and precision-guided similarity search modes — each tailored to different stages of the drug discovery pipeline.
|
|
Read more...
|
|

The OTAVA G9a Targeted Library comprises 561 carefully curated small molecules aimed at modulating the activity of histone methyltransferase G9a (EHMT2)—a master regulator of transcriptional repression through histone H3 lysine 9 (H3K9) methylation. This collection provides a powerful resource for researchers exploring epigenetics-driven mechanisms in cancer, neurodegeneration, inflammation, and stem cell reprogramming.
|
|
Read more...
|
|

The OTAVA MolGluesLike Compounds Library is a scientifically curated collection of 2750 small molecules designed to enable the discovery and development of molecular glues — a groundbreaking modality in drug discovery that stabilizes or induces protein-protein interactions (PPIs).
These specialized compounds have the potential to redefine therapeutic strategies by targeting previously “undruggable” proteins, offering exciting opportunities in areas such as oncology, immunology, and neurodegenerative disease research.
|
|
Read more...
|
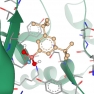
CHEMriya™ is an ultra-large combinatorial Chemical Space developed by OTAVA to transform hit expansion, hit-to-lead optimization, and compound evolution. Designed to accelerate drug discovery, CHEMriya provides access to a vast collection of chemically diverse molecules for pharmaceutical research and computational screening.
Explore CHEMriya on BioSolveIT
Start exploring via CHEESE Search
|
|
Read more...
|

The OTAVA Covalent Inhibitors Library is a meticulously curated collection of small-molecule covalent inhibitors, each designed to form stable, often irreversible, bonds with target proteins. These compounds feature nucleophile-sensitive functional groups that enable precise and selective inhibition, making them powerful tools in modern drug discovery.
Covalent inhibitors are widely recognized for their enhanced potency, prolonged target engagement, and unique therapeutic advantages, particularly in oncology, infectious diseases, neurodegenerative disorders, and enzyme-related conditions. By forming covalent interactions with critical amino acid residues such as cysteine, serine, lysine, and histidine, these compounds provide long-lasting inhibition that can overcome resistance mechanisms and improve drug efficacy.
|
|
Read more...
|
|

OTAVA's CELMoDs (Cereblon E3 Ligase Modulators) library represents a cutting-edge innovation in the field of targeted protein degradation. Building on the foundational breakthroughs of IMiDs (Immunomodulatory Drugs), PROTACs (Proteolysis Targeting Chimeras), and molecular glue technologies, this library focuses on compounds that harness and enhance cereblon (CRBN)-mediated degradation pathways. These compounds are meticulously designed to stabilize CRBN's closed conformation, facilitating selective and efficient degradation of disease-relevant target proteins.
|
|
Read more...
|
Embark on a new era of drug discovery as OTAVA’s CHEMRIYA™ Virtual Chemical Space integrates with CHEESE Search, the advanced AI-powered platform by Deep MedChem.
Unparalleled Chemical Diversity:
Access a subset of CHEMRIYA™, a next-generation virtual chemical space tailored for hit expansion, hit-to-lead, and lead optimization.
|
|
Read more...
|
|
 The COVID-19 pandemic caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is a global health emergency. An attractive drug target for this coronavirus is the main protease (3C-like proteinase, 3CLpro, Mpro) because of its essential role in processing the polyproteins that are translated from the viral RNA. The COVID-19 pandemic caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is a global health emergency. An attractive drug target for this coronavirus is the main protease (3C-like proteinase, 3CLpro, Mpro) because of its essential role in processing the polyproteins that are translated from the viral RNA.
|
|
Read more...
|
|
|

The OTAVA GPCR Agonist Library is a computationally refined collection built to explore GPCR-privileged chemical space with high scaffold diversity and strong agonist-like physicochemical profiles.
|
|
Read more...
|
|

In recent years, structured RNAs have become tractable drug targets, enabling the discovery of selective modulators for riboswitches, long noncoding RNAs, G-quadruplexes, and RNA–protein complexes.
Breakthrough advances in library design, screening methodologies, and AI-based prioritization have expanded the scope of RNA-targeted drug discovery (Kovachka et al., Nat Rev Chem 2024; Lundquist et al., SLAS Discovery 2025; Morishita, ChemMedChem 2022; Momentum Bio, 2024).
Modern RNA-focused screening now combines:
-
SPR/BLI for kinetic profiling and specificity ranking,
-
AI-guided virtual enrichment to prioritize compounds with high “RNA-likeness” before experimental testing (Graff et al., Chem Sci 2020; Cao et al., Nat Mach Intell 2023).
|
|
Read more...
|
|

Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1; also known as GON-10, RPD3, or KDAC1) is a key epigenetic regulator involved in chromatin remodeling and gene expression. Aberrant HDAC1 activity has been implicated in tumorigenesis, and it is widely recognized as a high-value target for cancer therapy due to its role in promoting oncogenic transcriptional programs.
The mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR; also referred to as FRAP1, RAFT1, or RAPT1) is a central serine/threonine kinase that integrates nutrient and growth factor signals to regulate cell growth, proliferation, metabolism, and autophagy. Hyperactivation of mTOR signaling is a hallmark of various malignancies, contributing to uncontrolled tumor cell survival and resistance to therapy.
|
|
Read more...
|
|

The Targeted AHR Modulator Library is a curated chemical screening set designed to accelerate the discovery of novel small-molecule modulators of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) — a ligand-dependent transcription factor with key roles in immunity, cancer, inflammation, and xenobiotic metabolism.
This unique compound library supports early-stage discovery, target validation, and therapeutic innovation by providing access to structurally diverse and computationally prioritized molecules tailored for AHR-centric research and drug development programs.
|
|
Read more...
|
|

SuFEx (Sulfur-Fluoride Exchange) Chemistry represents the next-generation approach to covalent drug discovery, chemical biology, and synthetic chemistry. Building on the principles of click chemistry, SuFEx reactions leverage the unique S(VI)–F bond, allowing precise and high-yielding chemical transformations under mild conditions.
OTAVA, in collaboration with Melius Organics, introduces a comprehensive SuFEx Handle Fragment Library, a diverse collection of aryl fluorosulfates and sulfamoyl fluorides designed to expand the druggable proteome, enhance covalent drug development, and facilitate advanced chemical synthesis.
|
|
Read more...
|
|

Tissue transglutaminase 2 (tTG2) is a multifunctional enzyme involved in extracellular matrix stabilization, cell adhesion, signal transduction, and protein crosslinking. It plays a pivotal role in various physiological processes, but its dysregulation has been implicated in multiple diseases, including celiac disease, fibrosis, cancer, and neurodegenerative disorders. Due to its involvement in disease progression, tTG2 is a prime target for drug discovery, yet the development of small-molecule inhibitors remains an underexplored frontier.
|
|
Read more...
|
|

The OTAVA USP30 Targeted Library is a cutting-edge collection of 624 meticulously curated chemical compounds designed for the identification and development of inhibitors targeting ubiquitin-specific protease 30 (USP30). By leveraging advanced computational methods and adhering to modern medicinal chemistry standards, this library offers researchers a unique toolset to explore therapeutic avenues for critical diseases.
|
|
Read more...
|
|

OTAVAchemicals Innovative Therapeutic Targets Library (2989 compounds in total) is designed to accelerate the discovery of inhibitors for key proteins, including farnesyl protein transferase (FPT), HIV-1 capsid protein p24 (GAG), exportin 1 (XPO1), and β-cardiac myosin 7 (MYH7). Developed using DrugBank and ZINC databases and incorporating machine learning for virtual screening, this library offers a curated collection of molecules for advancing drug development by enhancing screening efficiency and accuracy. 
|
|
Read more...
|
|
SARS-CoV-2 Targeted Libraries |
|
 The pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), which is caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is a serious global concern for public health with thousands of fatalities. Today, no specific drugs are available to treat this disease. Thus, there remains an urgent need for the development of specific antiviral therapeutics toward SARS-CoV-2. The pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), which is caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is a serious global concern for public health with thousands of fatalities. Today, no specific drugs are available to treat this disease. Thus, there remains an urgent need for the development of specific antiviral therapeutics toward SARS-CoV-2.
Read more... |
|
 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRP, RDR or RNA replicase) is an enzyme that catalyzes the replication of RNA from an RNA template. RdRPs play a vital role in the growth of RNA viruses and are important targets for antiviral drug development. RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRP, RDR or RNA replicase) is an enzyme that catalyzes the replication of RNA from an RNA template. RdRPs play a vital role in the growth of RNA viruses and are important targets for antiviral drug development.
|
|
Read more...
|
|
 HOME
HOME ABOUT
ABOUT
 SERVICES
SERVICES
 PRODUCTS
PRODUCTS
 Targeted Libraries
Targeted Libraries
 Biochemicals
Biochemicals
 RESEARCH
RESEARCH
 DOWNLOADS
DOWNLOADS ORDERING
ORDERING
 CONTACTS
CONTACTS



 It is proved that a diverse compound library is the most successful and straightforward starting point to find new leads. Moreover, it is the best way to enhance your research compound collections by adding new substances with different chemotypes.
It is proved that a diverse compound library is the most successful and straightforward starting point to find new leads. Moreover, it is the best way to enhance your research compound collections by adding new substances with different chemotypes.

















