HOME
HOME ABOUT
ABOUT
 SERVICES
SERVICES
 PRODUCTS
PRODUCTS
 Targeted Libraries
Targeted Libraries
- SARS-CoV-2 Targeted Libraries
- SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA Polymerase Targeted Library
- SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Targeted Library
- Machine Learning SARS Targeted Library
- SARS-CoV-2 NSP16 Targeted Library
- SARS-CoV-2 Papain-like ProteaseTargeted Library
- SARS-CoV-2 Helicase Targeted Library
- SARS-CoV-2 Endoribonuclease Targeted Library
- SARS-CoV-2 Nonstructural Protein 14 (NSP14) Targeted Library
- Protein-Protein Interaction
- AI-powered Libraries
- Disease-Based Libraries
- Covalent Inhibitors Library
- Innovative Therapeutic Targets Library
- Targeted CELMoDs Collection
- USP30 Targeted Library
- tTG2 Inhibitor Library
- AHR Modulator Library
- G9a Targeted Library
- Epigenetic Targets
- Peptidomimetics
- Glycomimetics
- Protein Kinases
- Proteases
- GPCRs
- Nuclear Receptors
- Ion Channels
- RNA Binding
- SH2 Binding
- General Activities
- Other
- All Focused Libraries
- SARS-CoV-2 Targeted Libraries
 Biochemicals
Biochemicals
 RESEARCH
RESEARCH
 DOWNLOADS
DOWNLOADS ORDERING
ORDERING
 CONTACTS
CONTACTS
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
September, 2025 UPDATE:
Newsletter Subscription
Stay updated with our new products and services. You can unsubscribe at any time.
|
|
All active compounds were tested for antimicrobial effect against M. tuberculosis H37Rv. The compound 1 seems to have the best cell permeability and inhibits growth of pathogenic bacteria with IC50 = 10.01 µM and IC90 = 13.53 µM. References:
Development of M. tuberculosis leucyl-tRNA synthetas inhibitors:
|
| ASK1 | Aurora A | FGFR1 | Tie2 | JNK3 | CK2 |
| 14 | 45 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 83 |
The inhibitory profiles of BPyO-34 were investigated on a small panel of protein kinases. These studies have demonstrated that BPyO-34 is a selective inhibitor of ASK1.
References:
- Identification of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1) inhibitors among the derivatives of benzothiazol-2-yl-3-hydroxy-5-phenyl-1,5-dihydro-pyrrol-2-one. Sergiy A. Starosyla, Galyna P. Volynets, Sergiy S. Lukashov, Oksana B. Gorbatiuk, Andriy G. Golub, Volodymyr G. Bdzhola, Sergiy M. Yarmoluk. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry. 2015, 23: 2489-2497.
Development of ASK1 Pharmacophore Model Derived from Diverse Classes of Inhibitors
The three-dimensional pharmacophore model of ASK1 inhibitors has been developed with PharmaGist program (Fig. 4). The positions of pharmacophore features in the model correspond to conformations of highly active ASK1 inhibitors in which they interact with ATP-binding site of ASK1.
Fig. 4. ASK1 inhibitors pharmacophore model
The generated pharmacophore model allows accurately predict active and inactive compounds and can be of great use for virtual screening aimed at discovering novel ASK1 inhibitors.
References:
- ASK1 pharmacophore model derived from diverse classes of inhibitors. Sergiy A. Starosyla, Galyna P. Volynets, Volodymyr G. Bdzhola, Andriy G. Golub, Mykola V. Protopopov, Sergiy M. Yarmoluk. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 2014, 24: 4418–4423.
Development of protein kinase ASK1 inhibitors:
5-(5-Phenyl-furan-2-ylmethylene)-2-thioxo-thiazolidin-4-ones
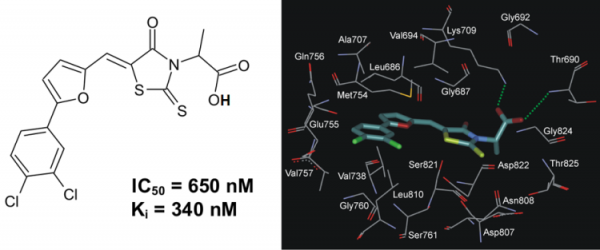
A series of 5-(5-Phenyl-furan-2-ylmethylene)-2-thioxo-thiazolidin-4-one derivatives has been synthesized and evaluated in vitro toward human protein kinase ASK1. It was revealed that compound 2-{5-[5-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-furan-2-ylmethylene]-4-oxo-2-thioxo-thiazolidin-3-yl}-propanoic acid (PFTA-1) inhibited ASK1 with a Ki of 340 nM (Fig. 5).
Fig. 5. The chemical structure of inhibitor PFTA-1 and its binding mode with ASK1 active site.
Table 3. Residual Activity of Protein Kinases (%) in the Presence of PFTA-1 at 10 μM Concentration
| ASK1 | Aurora A | HGFR | FGFR1 | Tie2 | JNK3 | CK2 |
| 3 | 14 | 65 | 88 | 29 | 46 | 34 |
The inhibitory profiles of PFTA-1 were investigated on a small panel of protein kinases. These studies have demonstrated that PFTA-1 is a selective inhibitor of ASK1.
References:
- Rational design of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 inhibitors: discovering novel structural scaffold. Volynets GP, Bdzhola VG, Golub AG, Synyugin AR, Chekanov MO, Kukharenko OP, Yarmoluk SM. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 61: 104-115.
Development of protein kinase CK2 inhibitors:
4`-hydroxyflavones
These novel synthetic flavone inhibitors (4`-hydroxyflavones) were identified with receptor-based virtual screening of combinatorial library of 150,000 organic compounds. Following in vitro tests revealed that 19 flavones out of 49 selected display ability to inhibit activity of CK2 (IC50 < 30 µM). After several cycles of their chemical optimization 31 new inhibitors with activity 0.004 µM – 8 µM have been obtained. The most active compound FNH79 (Fig. 6) have IC50 nearly 100 times higher than IC50 of fisetin, the most active natural flavone known to inhibit CK2. Initial selectivity tests of this compound using four serine/threonine (ASK1, JNK3, Aurora A, ROCK1) and three tyrosine protein kinases (FGFR1, Met, Tie2) as targets revealed negligible inhibitory activity towards these enzymes.
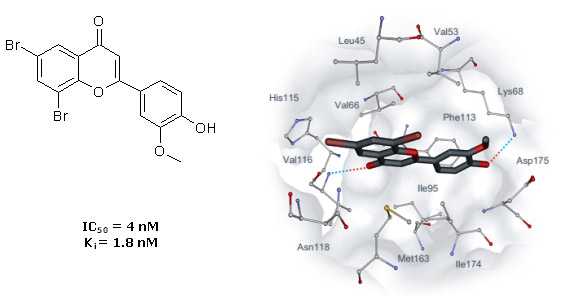
Fig. 6. Binding mode of flavone FNH79 obtained with molecular docking. Intermolecular hydrogen bonds are indicated with dotted lines.
Table 4. Kinase residual activity of FNH79, determined in the presence of 10 µM of inhibitor is expressed as a percentage of the control without inhibitor. Final concentration of ATP in the experiment was 100 µM.
|
Protein Kinase |
FNH79 |
|
CK2 |
0.8 |
References:
- Golub AG, Bdzhola VG, Ostrynska OV, Kyshenia IV, Sapelkin VM, Prykhod’ko AO, Kukharenko OP, Yarmoluk SM (2013) Discovery and characterization of synthetic 4’-hydroxyflavones – New CK2 inhibitors from flavone family. Bioorg Med Chem 21:6681-6689.
Development of protein kinase CK2 inhibitors:
4´-carboxyflavonols
Flavonol derivatives as new CK2 inhibitors were identified with virtual screening of 150,000 small organic compounds. In the course of selection, preference has been given to the compounds having carboxyl group. In vitro screening has shown that five carboxyl-containing flavones from 13 tested inhibit CK2 activity (IC50 is < 10 µM). Studying structure–activity relationships of these novel CK2 inhibitors, we analyzed the docking complexes for the 13 tested compounds and developed a binding model of the flavone derivatives in CK2 ATP-binding site. Based on these studies, extra 13 derivatives of 3-hydroxy-4´-carboxyflavone were synthesized and tested in vitro toward CK2. All tested compounds displayed submicromolar IC50 values, and two most active flavonol derivatives have Ki values 13 nM and 2.5 nM. Binding modes of these compounds were studied with docking and molecular dynamics simulation.

Fig. 7. Binding mode of FLC21. The complex has been obtained with molecular dynamics simulation. Intermolecular hydrogen bonds are shown as dotted lines.
Reference:
- Golub AG, Bdzhola VG, Kyshenia YV, Sapelkin VM, Prykhod'ko AO, Kukharenko OP, Ostrynska OV, Yarmoluk SM (2011) Structure-based discovery of novel flavonol inhibitors of human protein kinase CK2. Mol Cell Biochem 356(1-2):107-115.
Development of protein kinase CK2 inhibitors:
Thienopyrimidines
A novel series of substituted (thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-ylthio)carboxylic acids has been synthesized and tested in vitro towards human protein kinase CK2. It was revealed that the most active compound inhibiting CK2 is 3-{[5-(4-methylphenyl)thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl]thio}propanoic acid (IC50=0.1 µM). Structure-activity relationships of 28 tested thienopyrimidine derivatives have been studied and binding mode of this chemical class has been predicted. Evaluation of the inhibitors on seven protein kinases revealed considerable selectivity towards CK2.
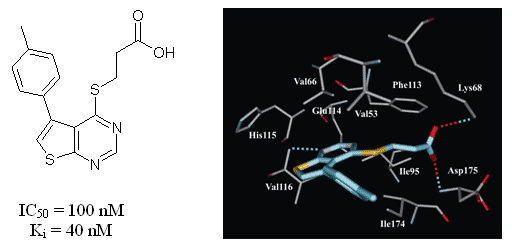
Fig. 8. The binding mode of thienopyrimidine inhibitor in the active site of the CK2 catalytic subunit. Hydrogen bonds are shown by the dotted lines.
References:
- Golub AG, Bdzhola VG, Briukhovetska NV, Balanda AO, Kukharenko OP, Kotey IM, Ostrynska OV, Yarmoluk SM (2011) Synthesis and biological evaluation of substituted (thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-ylthio)carboxylic acids as inhibitors of human protein kinase CK2. Eur J Med Chem 46(3):870-876.
Development of protein kinase ASK1 inhibitors:
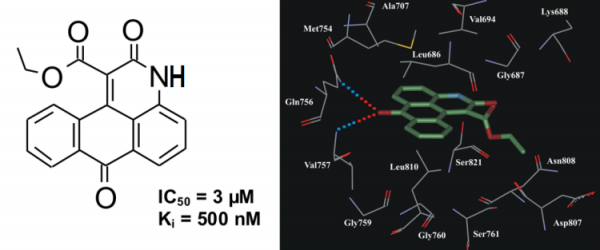
3H-naphtho[1,2,3-de]quinoline-2,7-diones
In vitro kinase assay revealed that derivatives of 3H-naphtho[1,2,3-de]quinoline-2,7-dione possess inhibitory activity towards ASK1. Compound ethyl 2,7-dioxo-2,7-dihydro-3H-naphtho[1,2,3-de]quinoline-1-carboxylate (NQDI-1) inhibited ASK1 with a Ki of 500 nM (Fig. 9). In our preliminary selectivity study this compound exhibited specific inhibitory activity towards ASK1 (Table 5).
Fig.9. The chemical structure of inhibitor NQDI-1 and its binding mode in ASK1 active site.
Table 5. Residual Activity of Protein Kinases (%) in the Presence of NQDI-1 at 25 μM Concentration
| ASK1 | Aurora A | ROCK | HGFR | FGFR1 | Tie2 | JNK3 | CK2 |
| 12.5 | 79 | 100 | 62 | 44 | 84 | 100 | 78 |
It was reported that NQDI-1 has prevented ROS-mediated apoptosis in the NG108-15 neuronal cell line (Nomura et al., Neurosci Lett. 2013, 549, 63). Moreover, the administration of NQDI-1 to laboratory animals attenuated renal dysfunction and histological changes characteristic for renal ischemia/reperfusion injury (El Eter, Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 2013, 11, 179). Therefore, inhibitor NQDI-1 has strong pharmacological potential.
References:
- Identification of 3H-naphtho[1,2,3-de]quinoline-2,7-diones as inhibitors of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1). Volynets GP, Chekanov MO, Synyugin AR, Golub AG, Kukharenko OP, Bdzhola VG, Yarmoluk SM. J Med Chem. 2011, 54(8):2680-2686.
Development of protein kinase CK2 inhibitors:
4,5,6,7-tetrahalogeno-1H-isoindole-1,3(2H)-diones
Here we present the 4,5,6,7-tetrahalogeno-1H-isoindole-1,3(2H)-diones (TID) as a novel potent class of CK2 inhibitors (Table 6). We identified this class of inhibitors by high-throughput docking of a compound collection in the ATP binding site of human CK2. The most active compounds are 2-(4,5,6,7-tetraiodo-1,3-dioxo-1,3-dihydro-2H-isoindol-2-yl)propanoic acid and 2-(4,5,6,7-tetraiodo-1,3-dioxo-1,3-dihydro-2H-isoindol-2-yl)acetic acid with IC50 values 0.15 µM and 0.3 µM, respectively. These inhibitors are ATP-competitive and they only minimally inhibit the activities of protein kinases DYRK1a, MSK1, GSK3 and CDK5 (Table 7). Binding modes for the most active inhibitors are proposed (Fig. 10).
Table 6. Structures and IC50 values of TID 43, 45, 46, 48, 58, 59.
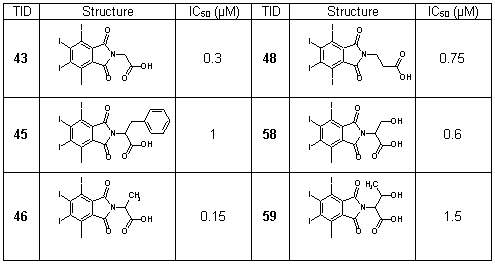
Table 7. Specificity spectrum of TID 43, 46, 48 and 58. Residual activity, determined in the presence of 10 µM inhibitor, is expressed as a percentage of the control without inhibitor. Final concentration of ATP in the experiment was 100 µM.
| Protein Kinase | TID43 | TID 46 | TID48 | TID 58 |
|
CK2 DYRK1a MSK1 GSK3 CDK5 |
11 80 64 >50 >50 |
7 83 70 >50 >50 |
15 60 78 >50 >50 |
18 70 76 >50 >50 |

Fig. 10. TID46-CK2 complex obtained by molecular docking. (A) General view. (B) Detailed view. Intermolecular hydrogen bonds are shown as dotted lines, their lengths (in Å) are indicated. Key hydrophobic interactions are indicated by arrows.
References:
- Golub AG, Yakovenko OYa, Prykhod'ko AO, Lukashov SS, Bdzhola VG, Yarmoluk SM (2008) Evaluation of 4,5,6,7-tetrahalogeno-1H-isoindole-1,3(2H)-diones as inhibitors of human protein kinase CK2. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1784(1): 143–149.
- Pat. UA69165 A, C07D215/00, 16.08.2004. Application of 4,5,6,7-tetrahalogeno-1,3-isoindolinediones as protein kinase CK2 inhibitors. Golub AG, Yakovenko OYa, Yarmoluk SM, Dubinina GG, Bdzhola VG, Prykhod’ko AO.
Development of protein kinase CK2 inhibitors:
3-carboxy-4(1H)-quinolones
This class of inhibitors (Fig. 11) has been selected via receptor-based virtual screening of the OTAVAchemicals compound library. It was revealed that the most active compounds, 5,6,8-trichloro-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid (7) (IC50 = 0.3 µM) and 4-oxo-1,4-dihydrobenzo[h]quinoline-3-carboxylic acid (9) (IC50 = 1 µM), are ATP competitive (Ki values are 0.06 µM and 0.28 µM, respectively). Evaluation of the inhibitors on seven protein kinases shows considerable selectivity toward CK2 (Table 8). According to theoretical calculations and experimental data, a structural model (Fig. 12) describing the key features of 3-carboxy-4(1H)-quinolones responsible for tight binding to CK2 active site has been developed.
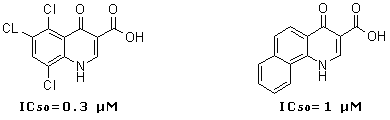
Fig. 11. 3-Carboxy-4-(1H)-Quinolones 7 and 9 - inhibitors of human Protein Kinase CK2
Table 8. Specificity spectrum of inhibitors 7 and 9. Residual activity determined in the presence of 10 µM inhibitor is expressed as a percentage of the control without inhibitor. Final concentration of ATP in the experiment was 100 µM.
| Protein Kinase | Inhibitor 7 | Inhibitor 9 |
|
CK2 JNK3 ROCK-I p56 LCK DYRK1a MSK1 GSK3 CDK5 |
11 74 85 87 35 71 >50 >50 |
25 81 78 80 85 89 >50 >50 |
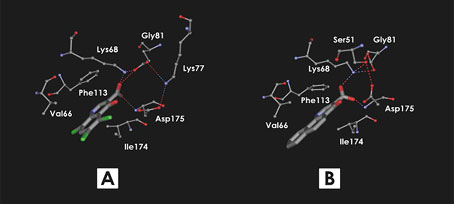
Fig. 12. Binding mode of 3-Carboxy-4-(1H)-Quinolones 7 (A) and 9 (B) predicted using flexible docking and molecular dynamics simulation
References:
- Golub AG, Yakovenko OY, Bdzhola VG, Sapelkin VM, Zien P, Yarmoluk SM (2006) Evaluation of 3-Carboxy-4(1H)-quinolones as Inhibitors of Human Protein Kinase CK2. J Med Chem 49(22):6443-6450.
- Pat. UA68984 A, C07D215/00, 16.08.2004. Application of 4-substituted 3-carboxyquinolines as protein kinase CK2 inhibitors. Sapelkin VM, Lukashov SS, Golub AG, Bdzhola VG, Yakovenko OYa, Yarmoluk SM, Dubinina GG.