|
 N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) are ligand-gated ion channels wich is activated by L-glutamate (the brain’s primary excitatory neurotransmitter). They have many critical roles in CNS function and in various neurological and psychiatric disorders. N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) are ligand-gated ion channels wich is activated by L-glutamate (the brain’s primary excitatory neurotransmitter). They have many critical roles in CNS function and in various neurological and psychiatric disorders.
We offer the chemical optimization service - synthesis of NMDARs targeted-specific sets of novel sulfonamides, quinazoline-4-ones, pyrazolines, iminothiazolidinones, N-arylbenzamides, coumarin-3-carboxylic acids, benzenesulfonamides, thiazoles and tetrahydroisoquinolines for your biological projects. These novel compounds will be selected from a sets of 1,000 - 2,000+ unique virtual derivatives for each chemical class using our company’s proprietary molecular modeling platform.
These target-specific sets of novel derivatives will be synthesized exclusively upon your request.
This is referred to a paper from Journal of Medicinal Chemistry* which showed that significant progress has been made in the development of selective positive and negative allosteric modulators (PAMs and NAMs) of NMDARs:
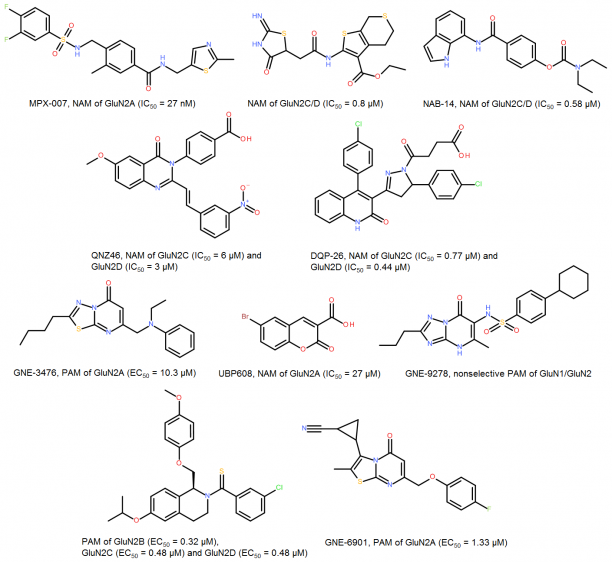
Novel derivatives of NAMs and PAMs provide a perfect basis for drug discovery projects related with pain, stroke, epilepsy, schizophrenia, post-traumatic stress disorder, depression and various neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
* Erica S. Burnell, Mark Irvine, Guangyu Fang, Kiran Sapkota, David E. Jane, Daniel T. Monaghan. Positive and Negative Allosteric Modulators of N‑Methyl‑D‑aspartate (NMDA) Receptors: Structure − Activity Relationships and Mechanisms of Action. J. Med. Chem. 2019, Vol. 62, pp. 3−23, DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b01640.
|
 HOME
HOME ABOUT
ABOUT
 SERVICES
SERVICES
 PRODUCTS
PRODUCTS
 Targeted Libraries
Targeted Libraries
 Biochemicals
Biochemicals
 RESEARCH
RESEARCH
 DOWNLOADS
DOWNLOADS ORDERING
ORDERING
 CONTACTS
CONTACTS