|
 Toxoplasmosis is a parasitic disease caused by Toxoplasma gondii. Approximately one-third of the population worldwide is chronically infected with T. gondii. First-line treatment of toxoplasmosis is a therapy based on dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR, DHFRP1, DYR) inhibitors which act on the folate metabolic pathway, thereby inhibiting T. gondii proliferation and survival. Toxoplasmosis is a parasitic disease caused by Toxoplasma gondii. Approximately one-third of the population worldwide is chronically infected with T. gondii. First-line treatment of toxoplasmosis is a therapy based on dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR, DHFRP1, DYR) inhibitors which act on the folate metabolic pathway, thereby inhibiting T. gondii proliferation and survival.
Our company offers the chemical optimization service - synthesis of a unique DHFR targeted set of novel arylpiperazine derivatives for your biological projects, related to developing of anti-toxoplasmosis drugs. These novel compounds could be selected from a set of 1,000+ exclusive virtual arylpiperazines using our company’s proprietary molecular modeling platform ODDA™.
This target-specific set of novel arylpiperazine derivatives will be synthesized exclusively upon your request.
A recent paper from the Journal of Medicinal Chemistry* showed that authors synthesized a series of arylpiperazines through structural modification of TRC-19 (a lead compound from their previous study, IC50 = 8.76 nM). Among them, compound 3 (5-(4-(3-(2-methoxypyrimidin-5-yl)phenyl)piperazin-1-yl)pyrimidine-2,4-diamine) showed activity against dihydrofolate reductase of T. gondii (IC50 = 1.57 nM) and good selectivity ratio between Human DHFR and Toxoplasma DHFR:
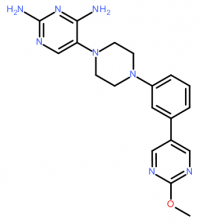
Compound 3, TgDHFR inhibitor, IC50 = 1.57 nM
Design and synthesis of novel arylpiperazines is a promising direction in toxoplasmosis treatment.
* Allen Hopper, Adam Brockman, Andy Wise, Julie Gould, Jennifer Barks, Joshua B Radke, L. David Sibley, Yongmao Zou, Stephen Thomas. Discovery of Selective Toxoplasma gondii Dihydrofolate Reductase Inhibitors for the Treatment of Toxoplasmosis. J. Med. Chem. 2019, Vol. 62(3), pp. 1562−1576, DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b01754.
|
 HOME
HOME ABOUT
ABOUT
 SERVICES
SERVICES
 PRODUCTS
PRODUCTS
 Targeted Libraries
Targeted Libraries
 Biochemicals
Biochemicals
 RESEARCH
RESEARCH
 DOWNLOADS
DOWNLOADS ORDERING
ORDERING
 CONTACTS
CONTACTS