|
 Autotaxin is a specific member of the ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase (NPP2 or ENPP2) family of enzymes that are important for generating the lipid signaling molecule lysophosphatidic acid (LPA). The activity of the secreted phosphodiesterase autotaxin produces the inflammatory signaling molecule LPA and has been associated with a number of human diseases including idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). Autotaxin is a specific member of the ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase (NPP2 or ENPP2) family of enzymes that are important for generating the lipid signaling molecule lysophosphatidic acid (LPA). The activity of the secreted phosphodiesterase autotaxin produces the inflammatory signaling molecule LPA and has been associated with a number of human diseases including idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF).
Our company is offering the synthesis a series of novel (R)-N-(1-(1-(1H-Indazol-5-yl)-3-methyl-2,4-dioxo-1,3,8-triazaspiro[4.5]decan-8-yl)-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl)-2-fluoro-5-(trifluoromethyl)benzamide derivatives as promising autotaxin inhibitors. A set of novel small compounds will be synthesized exclusively upon your request.
In a recent paper from the J. Med. Chem. 2020*, scientists demonstrated that X-165 is a potent, selective, and bioavailable small molecule inhibitor of the LPA synthetic phosphodiesterase, autotaxin:
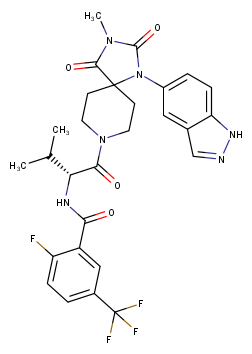
C28H28F4N6O4
X-165
pIC50 7.3 (IC50 5.5x10-8 M)
Design and synthesis of small compounds with the high inhibition potency against autotaxin is a perspective area to discover new bioactive compounds for treatment of diseases caused by ATX-LPA signaling disorders.
*J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 14, 7840–7856; DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c00688
|
 HOME
HOME ABOUT
ABOUT
 SERVICES
SERVICES
 PRODUCTS
PRODUCTS
 Targeted Libraries
Targeted Libraries
 Biochemicals
Biochemicals
 RESEARCH
RESEARCH
 DOWNLOADS
DOWNLOADS ORDERING
ORDERING
 CONTACTS
CONTACTS