|

Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a complex neurodegenerative disorder of the central nervous system that usually starts slowly and gets worse over time. It is characterized by progressive loss of dementia, cognitive ability, and eventually death. Currently there is no cure for the disease.
In the last two decades, several pharmacological strategies have emerged, including cholinergic and noncholinergic interventions. The design of novel inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase (AChE) has been mostly driven by the pivotal finding that AChE can bind the β-amyloid peptide (Aβ), thereby promoting Aβ aggregation as an early event in the neurodegenerative cascade of AD.
Also beta-secretase 1 (beta-site amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme 1, beta-site APP cleaving enzyme 1, BACE-1) is a promising therapeutic target to interventions for AD. It is known that this enzyme is involved in cleaving the amyloid precursor protein (APP) generating the Aβ peptides and catalyzes the rate-limiting step in the sequence.
We offer Alzheimer's Disease Targeted Polypharmacology Library (504 compounds in total), which is a special screening library that contains compounds with predicted inhibitory activity against both AChE and BACE-1. The library has been carefully designed with combined approach that included pharmacophore modeling, molecular docking and Bayesian modeling. General scheme is presented below:
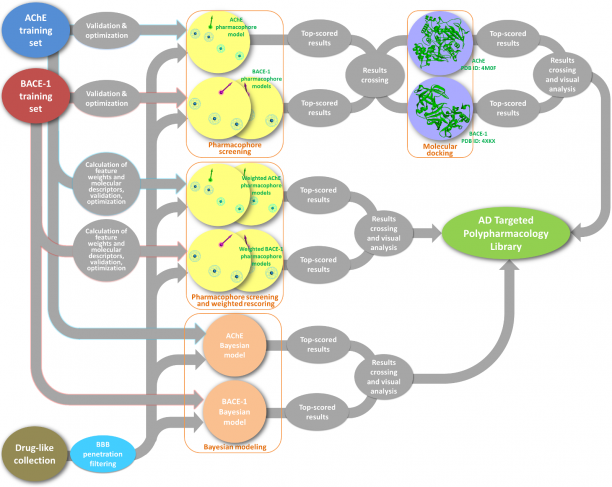
Please click on the scheme to enlarge it.
This library contains drug-like compounds with physicochemical properties preferable for BBB penetration and provides an excellent basis for screening in AD-associated research and drug development projects.
All compounds are in stock, cherry-picking is available.
The Alzheimer's Disease Targeted Polypharmacology Library (DB, SD, XLS, PDF format) as well as the price-list is available on request. Feel free to contact us or use on-line form below to send an inquiry if you are interested to obtain this library or if you need more information.
|
 HOME
HOME ABOUT
ABOUT
 SERVICES
SERVICES
 PRODUCTS
PRODUCTS
 Targeted Libraries
Targeted Libraries
 Biochemicals
Biochemicals
 RESEARCH
RESEARCH
 DOWNLOADS
DOWNLOADS ORDERING
ORDERING
 CONTACTS
CONTACTS



