Although insulin resistance and insulin secretory defects play a major role in the pathogenesis of hyperglycemia, several other metabolic defects contribute to the initiation/worsening of the diabetic state. Prominent among these is increased renal glucose reabsorption, which is maladaptive in patients with diabetes. Instead of an increase in renal glucose excretion, which could ameliorate hyperglycemia, there is an increase in renal glucose reabsorption, which helps sustain hyperglycemia [2].
OTAVAchemicals offers Sodium Glucose Cotransporter 2 Targeted Library (674 compounds in total), which is a special screening library that contains compounds with predicted SGLT2 inhibitory activity.
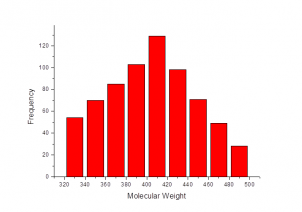
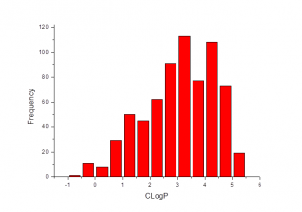
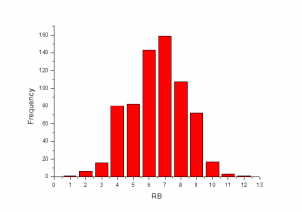
The compounds have been selected with two Bayesian models based on most active template compounds (SGLT2 inhibitors) taken from ChEMBL database. The first model was based on FCFP6 fingerprints, the second one – on ECFP6. Molecular descriptors, such as LogP, molecular weight, number of hydrogen donors and acceptors, number of rotatable bonds, number of rings and molecular polar surface area were involved in the construction of the models for more accuracy.
At the final stage, OTAVAchemicals Screening Compounds Collection was screened against these models and top-scored compounds were selected.
Thus, the compounds from the Sodium Glucose Cotransporter 2 Targeted Library match physical and structural parameters of typical sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors and contain important molecular fragments, required for SGLT2 binding.
This library provides an excellent basis for antidiabetic drug discovery projects.
-
Novikov A, Vallon V., Sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition in the diabetic kidney: an update, Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2016 Jan;25(1):50-8. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0000000000000187.
-
Mudaliar S, Polidori D, Zambrowicz B, Henry RR, Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter Inhibitors: Effects on Renal and Intestinal Glucose Transport: From Bench to Bedside, Diabetes Care. 2015 Dec;38(12):2344-53. doi: 10.2337/dc15-0642.
 HOME
HOME ABOUT
ABOUT
 SERVICES
SERVICES
 PRODUCTS
PRODUCTS
 Targeted Libraries
Targeted Libraries
 Biochemicals
Biochemicals
 RESEARCH
RESEARCH
 DOWNLOADS
DOWNLOADS ORDERING
ORDERING
 CONTACTS
CONTACTS