|
 The IDH1 (isocitrate dehydrogenase (NADP+) 1, HEL-216, HEL-S-26, IDCD, IDH, IDP, IDPC, PICD) is an enzyme which catalyze the oxidative decarboxylation of isocitrate to 2-oxoglutarate. Mutations at the arginine residue (R132) in IDH1 are frequently identified in various human cancers. Inhibition of this mutated dehydrogenase (mIDH1) with small molecules has been clinically validated as a promising therapeutic treatment for multiple solid tumors and acute myeloid leukemia. The IDH1 (isocitrate dehydrogenase (NADP+) 1, HEL-216, HEL-S-26, IDCD, IDH, IDP, IDPC, PICD) is an enzyme which catalyze the oxidative decarboxylation of isocitrate to 2-oxoglutarate. Mutations at the arginine residue (R132) in IDH1 are frequently identified in various human cancers. Inhibition of this mutated dehydrogenase (mIDH1) with small molecules has been clinically validated as a promising therapeutic treatment for multiple solid tumors and acute myeloid leukemia.
We offer the chemical optimization service - synthesis of mIDH1 targeted set of quinolinone derivatives for developing of isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 inhibitors. These novel compounds will be selected from a set of 3,000+ virtual quinolinones using our company’s proprietary molecular modeling platform ODDA™, synthesized and provided for your biological projects.
This is referred to a paper from Journal of Medicinal Chemistry* which showed that authors discovered mIDH1 inhibitors. Compound 63 ((S)-2-((1-(6-Chloro-2-oxo-1,2-dihydroquinolin-3-yl)ethyl)amino)-4-methoxypyrimidine-5-carbonitrile) possess good inhibition activity against this enzyme and efficacious in the mouse mIDH1 tumor xenograft model with a robust reduction of the tumor-derived 2-HG level, which is a PD biomarker of mIDH1 activity:
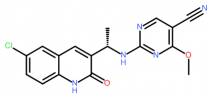
Compound 63, mIDH1 R132H IC50 = 18.4 nM, mIDH1 R132C IC50 = 13 nM
Design and synthesis of mIDH1 inhibitors is a promising direction in anticancer drug development.
* Jian Lin et al. Discovery and Optimization of Quinolinone Derivatives as Potent, Selective, and Orally Bioavailable Mutant Isocitrate Dehydrogenase 1 (mIDH1) Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2019, Vol. 62(14), pp. 6575-6596, DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b00362.
|
 HOME
HOME ABOUT
ABOUT
 SERVICES
SERVICES
 PRODUCTS
PRODUCTS
 Targeted Libraries
Targeted Libraries
 Biochemicals
Biochemicals
 RESEARCH
RESEARCH
 DOWNLOADS
DOWNLOADS ORDERING
ORDERING
 CONTACTS
CONTACTS