|

In recent years, structured RNAs have become tractable drug targets, enabling the discovery of selective modulators for riboswitches, long noncoding RNAs, G-quadruplexes, and RNA–protein complexes.
Breakthrough advances in library design, screening methodologies, and AI-based prioritization have expanded the scope of RNA-targeted drug discovery (Kovachka et al., Nat Rev Chem 2024; Lundquist et al., SLAS Discovery 2025; Morishita, ChemMedChem 2022; Momentum Bio, 2024).
Modern RNA-focused screening now combines:
-
SPR/BLI for kinetic profiling and specificity ranking,
-
AI-guided virtual enrichment to prioritize compounds with high “RNA-likeness” before experimental testing (Graff et al., Chem Sci 2020; Cao et al., Nat Mach Intell 2023).
|
|
Read more...
|
|
|

Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1; also known as GON-10, RPD3, or KDAC1) is a key epigenetic regulator involved in chromatin remodeling and gene expression. Aberrant HDAC1 activity has been implicated in tumorigenesis, and it is widely recognized as a high-value target for cancer therapy due to its role in promoting oncogenic transcriptional programs.
The mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR; also referred to as FRAP1, RAFT1, or RAPT1) is a central serine/threonine kinase that integrates nutrient and growth factor signals to regulate cell growth, proliferation, metabolism, and autophagy. Hyperactivation of mTOR signaling is a hallmark of various malignancies, contributing to uncontrolled tumor cell survival and resistance to therapy.
|
|
Read more...
|
|
|

SuFEx (Sulfur-Fluoride Exchange) Chemistry represents the next-generation approach to covalent drug discovery, chemical biology, and synthetic chemistry. Building on the principles of click chemistry, SuFEx reactions leverage the unique S(VI)–F bond, allowing precise and high-yielding chemical transformations under mild conditions.
OTAVA, in collaboration with Melius Organics, introduces a comprehensive SuFEx Handle Fragment Library, a diverse collection of aryl fluorosulfates and sulfamoyl fluorides designed to expand the druggable proteome, enhance covalent drug development, and facilitate advanced chemical synthesis.
|
|
Read more...
|
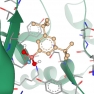
CHEMriya™ is an ultra-large combinatorial Chemical Space developed by OTAVA to transform hit expansion, hit-to-lead optimization, and compound evolution. Designed to accelerate drug discovery, CHEMriya provides access to a vast collection of chemically diverse molecules for pharmaceutical research and computational screening.
Explore CHEMriya on BioSolveIT
Start exploring via CHEESE Search
|
|
Read more...
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Page 4 of 16 |
 HOME
HOME ABOUT
ABOUT
 SERVICES
SERVICES
 PRODUCTS
PRODUCTS
 Targeted Libraries
Targeted Libraries
 Biochemicals
Biochemicals
 RESEARCH
RESEARCH
 DOWNLOADS
DOWNLOADS ORDERING
ORDERING
 CONTACTS
CONTACTS

 OTAVAchemicals offers a number of
OTAVAchemicals offers a number of 


