 Natural Product-Like Library Natural Product-Like Library has been designed as a special screening library containing synthetic compounds similar to natural products.
|
|
Read more...
|
|
 Catechol O‑Methyl Transferase (COMT, HEL-S-98n) degrades catecholamines, catecholestrogens and various drugs having a catechol structure. Mutation of COMT is associated with obsessive-compulsive disorder in men, anxiety phenotypes in women, schizophrenia and other. Developing of the COMT inhibitors is a promising area of neuropsychiatric research. Also catechol‐O‐methyltransferase inhibitors are used as adjuvants to the levodopa/AADC inhibitor therapy for Parkinson's disease treatment. Catechol O‑Methyl Transferase (COMT, HEL-S-98n) degrades catecholamines, catecholestrogens and various drugs having a catechol structure. Mutation of COMT is associated with obsessive-compulsive disorder in men, anxiety phenotypes in women, schizophrenia and other. Developing of the COMT inhibitors is a promising area of neuropsychiatric research. Also catechol‐O‐methyltransferase inhibitors are used as adjuvants to the levodopa/AADC inhibitor therapy for Parkinson's disease treatment.
|
|
Read more...
|
|
 Enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2, ENX-1, ENX1, EZH1, EZH2b, KMT6, KMT6A, WVS, WVS2, enhancer of zeste 2 polycomb repressive complex 2 subunit) is a histone-lysine N-methyltransferase. This enzyme plays an important role in histone methylation and, ultimately, transcriptional repression. Enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2, ENX-1, ENX1, EZH1, EZH2b, KMT6, KMT6A, WVS, WVS2, enhancer of zeste 2 polycomb repressive complex 2 subunit) is a histone-lysine N-methyltransferase. This enzyme plays an important role in histone methylation and, ultimately, transcriptional repression.
Mutation or over-expression of EZH2 has been linked to many forms of cancer, including bladder, uterine, breast, prostate and renal cancers. EZH2 inhibits genes responsible for suppressing of tumor development, and blocking of it activity may slow tumor growth. Therefore, EZH2 is an attractive target for anti-cancer therapy.
|
|
Read more...
|
|
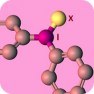 Diaryliodonium salts are well-known to transfer an aryl group to carbon and heteroatom nucleophiles, and in some cases a base is required [1]. However, transition metal catalysts and supporting ligands are not needed. Moreover, reactions conducted with diaryliodonium salts are operationally simple because they are non-toxic and are not sensitive to air or moisture. Therefore diaryliodonium salts offer an important alternative to metal-catalyzed arylation reactions. Despite these attractive characteristics, a major obstacle to their adoption in chemical synthesis and discovery chemistry has been commercial availability. Diaryliodonium salts are well-known to transfer an aryl group to carbon and heteroatom nucleophiles, and in some cases a base is required [1]. However, transition metal catalysts and supporting ligands are not needed. Moreover, reactions conducted with diaryliodonium salts are operationally simple because they are non-toxic and are not sensitive to air or moisture. Therefore diaryliodonium salts offer an important alternative to metal-catalyzed arylation reactions. Despite these attractive characteristics, a major obstacle to their adoption in chemical synthesis and discovery chemistry has been commercial availability.
|
|
Read more...
|
|
 Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 (S1PR1, S1P receptor 1, S1P1, endothelial differentiation gene 1, EDG1) is a G-protein-coupled receptor which binds the bioactive signaling molecule sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P). S1PR1 has an important role in regulating endothelial cell cytoskeletal structure, migration, vascular maturation and capillary-like network formation. Also S1PR1 signaling is important in the regulation of lymphocyte maturation, migration and trafficking. Abnormal functioning of S1PR1 is associated with cancer and multiple sclerosis. Agonists and antagonists of this receptor may have therapeutic potential in the treatment of such diseases. Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 (S1PR1, S1P receptor 1, S1P1, endothelial differentiation gene 1, EDG1) is a G-protein-coupled receptor which binds the bioactive signaling molecule sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P). S1PR1 has an important role in regulating endothelial cell cytoskeletal structure, migration, vascular maturation and capillary-like network formation. Also S1PR1 signaling is important in the regulation of lymphocyte maturation, migration and trafficking. Abnormal functioning of S1PR1 is associated with cancer and multiple sclerosis. Agonists and antagonists of this receptor may have therapeutic potential in the treatment of such diseases.
|
|
Read more...
|
|
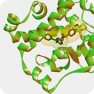 The Retinoic Acid Receptor-related Orphan Receptor-γ (RORγ, RORc, NR1F3, RORG, RZR-GAMMA, RZRG, TOR or IMD42) plays an important role in metabolism, inimmunity and circadian rhythm. Abnormal functioning of RORγ is associated with inflammatory, immune and skin diseases including psoriasis. Antagonists and inverse agonists of this receptor may have therapeutic potential in the treatment of such diseases. The Retinoic Acid Receptor-related Orphan Receptor-γ (RORγ, RORc, NR1F3, RORG, RZR-GAMMA, RZRG, TOR or IMD42) plays an important role in metabolism, inimmunity and circadian rhythm. Abnormal functioning of RORγ is associated with inflammatory, immune and skin diseases including psoriasis. Antagonists and inverse agonists of this receptor may have therapeutic potential in the treatment of such diseases.
|
|
Read more...
|
|
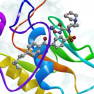 The Matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP2, gelatinase A, 72 kDa type IV collagenase) is involved in different functions such as reconstruction of the vasculature, angiogenesis, tissue repair, inflammation, tumor invasion and atherosclerotic plaque rupture. Mutations in the MMP2 gene are associated with Torg-Winchester syndrome, arthritis syndrome, multicentric osteolysis and other pathologies. Therefore, small molecule compounds targeting metalloproteinase-2 may be potential treatment for a variety of diseases related to abnormality functioning of MMP2. The Matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP2, gelatinase A, 72 kDa type IV collagenase) is involved in different functions such as reconstruction of the vasculature, angiogenesis, tissue repair, inflammation, tumor invasion and atherosclerotic plaque rupture. Mutations in the MMP2 gene are associated with Torg-Winchester syndrome, arthritis syndrome, multicentric osteolysis and other pathologies. Therefore, small molecule compounds targeting metalloproteinase-2 may be potential treatment for a variety of diseases related to abnormality functioning of MMP2.
|
|
Read more...
|
|
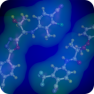 Selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs) act on the androgen receptors (ARs) in a tissue-selective manner and provide an opportunity to promote the beneficial effects of androgens in target tissues with greatly reduced unwanted side-effects. SARMs have been proposed as treatments of choice for various diseases, including muscle-wasting, breast cancer, and osteoporosis. Selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs) act on the androgen receptors (ARs) in a tissue-selective manner and provide an opportunity to promote the beneficial effects of androgens in target tissues with greatly reduced unwanted side-effects. SARMs have been proposed as treatments of choice for various diseases, including muscle-wasting, breast cancer, and osteoporosis.
|
|
Read more...
|
|
 Caspase 2 (CASP2, CASP-2, ICH1, NEDD-2, NEDD2, PPP1R57) is an initiator caspase for cellular apoptosis. It is also involved in several other vital processes including oxidative stress responses, regulation of cell cycle checkpoints, autophagy and senescence. Disorders of CASP2 activity are observed at obesity, metabolic syndrome, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and cancer [1, 2]. Therefore, small molecule compounds modulating CASP2 activity may have significant therapeutic potential. Caspase 2 (CASP2, CASP-2, ICH1, NEDD-2, NEDD2, PPP1R57) is an initiator caspase for cellular apoptosis. It is also involved in several other vital processes including oxidative stress responses, regulation of cell cycle checkpoints, autophagy and senescence. Disorders of CASP2 activity are observed at obesity, metabolic syndrome, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and cancer [1, 2]. Therefore, small molecule compounds modulating CASP2 activity may have significant therapeutic potential.
|
|
Read more...
|
|
 Selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) are compounds that act on the estrogen receptors (ERs). A characteristic that distinguishes these substances from pure ER antagonists and agonists (silent antagonists and full agonists) is that their action is different in various tissues, thereby granting the possibility to selectively inhibit or stimulate estrogen-like action in various tissues. Selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) are compounds that act on the estrogen receptors (ERs). A characteristic that distinguishes these substances from pure ER antagonists and agonists (silent antagonists and full agonists) is that their action is different in various tissues, thereby granting the possibility to selectively inhibit or stimulate estrogen-like action in various tissues.
|
|
Read more...
|
|
|
 The PDZ domains play key roles in anchoring receptor proteins in the membrane to cytoskeletal components, different intracellular signal transduction pathways and many human diseases are associated with their dysregulation. The PDZ domains play key roles in anchoring receptor proteins in the membrane to cytoskeletal components, different intracellular signal transduction pathways and many human diseases are associated with their dysregulation.
|
|
Read more...
|
|
 Lysine-specific demethylase 4C (GASC1, KDM4C, JHDM3C, JMJD2C, TDRD14C, bA146B14.1) is a histone demethylase that specifically demethylates 'Lys-9' and 'Lys-36' residues of histone H3, thereby plays a central role in histone modification. Abnormal functioning of this epigenetic factor is associated with different cancers, including breast cancer. Targeted inhibition of GASC1 in cancer opens new avenues for therapeutic development. Lysine-specific demethylase 4C (GASC1, KDM4C, JHDM3C, JMJD2C, TDRD14C, bA146B14.1) is a histone demethylase that specifically demethylates 'Lys-9' and 'Lys-36' residues of histone H3, thereby plays a central role in histone modification. Abnormal functioning of this epigenetic factor is associated with different cancers, including breast cancer. Targeted inhibition of GASC1 in cancer opens new avenues for therapeutic development.
|
|
Read more...
|
|
 Cathepsin K (CTSK, CTS02, CTSO, CTSO1, CTSO2, PKND, PYCD) is a lysosomal cysteine protease involved in bone remodeling and resorption. It has a major role in osteoporosis and other bone-related pathologies, cancer, diabetes, obesity and atherosclerosis. Cathepsin K inhibitors show great potential in the treatment of such diseases. Cathepsin K (CTSK, CTS02, CTSO, CTSO1, CTSO2, PKND, PYCD) is a lysosomal cysteine protease involved in bone remodeling and resorption. It has a major role in osteoporosis and other bone-related pathologies, cancer, diabetes, obesity and atherosclerosis. Cathepsin K inhibitors show great potential in the treatment of such diseases.
|
|
Read more...
|
|
 Our company is currently offering about 100 new quaternary ammonium salts that could be of interest to your research. All quaternary ammonium salts are in stock, and a full list of the salts in our catalog is available upon request. Our company is currently offering about 100 new quaternary ammonium salts that could be of interest to your research. All quaternary ammonium salts are in stock, and a full list of the salts in our catalog is available upon request.
Synthetic experience of Otava chemists allows to carry out custom syntheses of even more complex structures of quaternary ammonium salts at a reasonable price.
|
|
Read more...
|
|
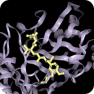 The Renin (REN, HNFJ2) is an aspartic protease (also known as an angiotensinogenase). It participates in arterial vasoconstriction and the body's renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system (RAAS) that mediates the volume of extracellular fluid (blood plasma, lymph and interstitial fluid). Thus, it regulates the body's mean arterial blood pressure. An over-active RAAS leads to vasoconstriction and retention of sodium and water. These effects cause hypertension. Therefore, renin inhibitors can be used for the treatment of hypertension. The Renin (REN, HNFJ2) is an aspartic protease (also known as an angiotensinogenase). It participates in arterial vasoconstriction and the body's renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system (RAAS) that mediates the volume of extracellular fluid (blood plasma, lymph and interstitial fluid). Thus, it regulates the body's mean arterial blood pressure. An over-active RAAS leads to vasoconstriction and retention of sodium and water. These effects cause hypertension. Therefore, renin inhibitors can be used for the treatment of hypertension.
|
|
Read more...
|
|
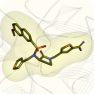 Kallikrein 6 (KLK6, hK6, Bssp, Klk7, PRSS18, PRSS9, SP59, kallikrein related peptidase 6) plays an important role in various physiological processes. Disorders of KLK6 activity are observed at cancer and neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease and multiple sclerosis. Therefore, small molecule compounds modulating kallilrein 6 activity may have a significant therapeutic potential. Kallikrein 6 (KLK6, hK6, Bssp, Klk7, PRSS18, PRSS9, SP59, kallikrein related peptidase 6) plays an important role in various physiological processes. Disorders of KLK6 activity are observed at cancer and neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease and multiple sclerosis. Therefore, small molecule compounds modulating kallilrein 6 activity may have a significant therapeutic potential.
|
|
Read more...
|
|
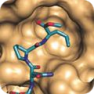 The interaction of proteins are critical to nearly all biological processes, including cellular signaling [1]. We offer special screening Peptidomimetic Libraries: β-Turn Peptidomimetic Library containing synthetic compounds which mimic beta-turns of proteins and a-Helix Peptidomimetic Library of compounds mimic alpha-helixes of proteins. These libraries are intended for research and drug discovery projects focused on protein-protein interactions. The interaction of proteins are critical to nearly all biological processes, including cellular signaling [1]. We offer special screening Peptidomimetic Libraries: β-Turn Peptidomimetic Library containing synthetic compounds which mimic beta-turns of proteins and a-Helix Peptidomimetic Library of compounds mimic alpha-helixes of proteins. These libraries are intended for research and drug discovery projects focused on protein-protein interactions.
|
|
Read more...
|
|
 To facilitate a process of finding new agrochemicals within the fields of weed, pest and disease control, OTAVAchemicals design a set of focused libraries of diverse compounds for agrochemical research and development. To facilitate a process of finding new agrochemicals within the fields of weed, pest and disease control, OTAVAchemicals design a set of focused libraries of diverse compounds for agrochemical research and development.
Read more... |
|
 The GABA receptors (GABAA and GABAB) respond to the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), the chief inhibitory compound in the mature vertebrate central nervous system. GABA receptors agonists produce typically sedative effects, and may also cause other effects such as anticonvulsant, anxiolytic and muscle relaxant effects. Antagonists of GABA receptors inhibit the action of GABA. In general they produce stimulant and convulsant effects. Therefore, small molecule compounds modulating GABA receptors activity may have significant therapeutic potential. The GABA receptors (GABAA and GABAB) respond to the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), the chief inhibitory compound in the mature vertebrate central nervous system. GABA receptors agonists produce typically sedative effects, and may also cause other effects such as anticonvulsant, anxiolytic and muscle relaxant effects. Antagonists of GABA receptors inhibit the action of GABA. In general they produce stimulant and convulsant effects. Therefore, small molecule compounds modulating GABA receptors activity may have significant therapeutic potential.
|
|
Read more...
|
|
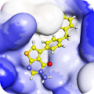 Beta-arrestins (ß-arrestin 1 and ß-arrestin 2) play central roles in the mechanisms regulating G protein-coupled receptors signalling and trafficking. They participate in agonist-mediated desensitization of GPCR and cause specific dampening of cellular responses to stimuli such as sensory signals, hormones or neurotransmitters [1]. Beta-arrestins (ß-arrestin 1 and ß-arrestin 2) play central roles in the mechanisms regulating G protein-coupled receptors signalling and trafficking. They participate in agonist-mediated desensitization of GPCR and cause specific dampening of cellular responses to stimuli such as sensory signals, hormones or neurotransmitters [1].
|
|
Read more...
|
|
 HOME
HOME ABOUT
ABOUT
 SERVICES
SERVICES
 PRODUCTS
PRODUCTS
 Targeted Libraries
Targeted Libraries
 Biochemicals
Biochemicals
 RESEARCH
RESEARCH
 DOWNLOADS
DOWNLOADS ORDERING
ORDERING
 CONTACTS
CONTACTS


 Natural Product-Like Library has been designed as a special screening library containing synthetic compounds similar to natural products.
Natural Product-Like Library has been designed as a special screening library containing synthetic compounds similar to natural products.


















